Managing all aspects of a product or service, from procurement to sale, from finances to the flow of goods, has resulted in an entire industry being built – the industry of supply chain management and supply chain logistics. By effectively managing the flow of goods, information, and resources from suppliers to end consumers, organizations can streamline processes, minimize costs, and optimize inventory levels, ultimately improving operational efficiency across the board. This article will be looking at the beginner’s guide to what supply chain management is, how it works, as well as its basic components.
What is Supply Chain Management?
As explained briefly above, supply chain management is the overseeing of all processes a product or service goes through to become the final product or service, ready to be delivered to the consumer market. This includes the various supply chain steps from procurement to sales, as well as the planning, logistics, and financial aspects that go along with it. Some of these features might include procurement, production, transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and customer service.
However, supply chain management’s responsibilities run deeper than the general overseeing and management of activities involved in the flow of goods, it additionally plays an important role in optimizing these processes. Creating a smoother-running supply chain can result in minimized costs, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction. Operational efficiency is further maximized when the collaboration among various stakeholders at different levels and phases of the supply chain is strong, and constantly reinforced.
Basic Components of Supply Chain Management
There are a number of basic components that can be expected to be found across any company’s supply chain. These might include some of the previously mentioned steps such as planning, sourcing, manufacturing, delivery, and return or reverse logistics. Let us break these various components down into what they consist of, as well as their importance within the supply chain! This segment should also reveal how much responsibility and importance lies within the supply chain.
Planning: Very much explained by the name of this component, planning involves forecasting and determining the demand for products or services in order to be able to develop production schedules and establish inventory levels accordingly. Accurately forecasting demand helps organizations optimize their production and procurement activities, ensuring that the right amount of products or services is available at the right time. The knock-on effects of a strong planning phase are great, resulting in minimized stock-outs or excess inventory, which further leads to reduced holding and waste costs, and additionally, improved customer satisfaction from reliable and quick service.
Sourcing: Sourcing does not only include the procurement of raw materials, but identifying and selecting the suppliers providing these raw materials, negotiating their contracts, and managing and maintaining strong relationships with them. Suppliers should be evaluated based on criteria inclusive of quality, reliability, cost, and ethical practices. Once strong relationships are established, organizations are able to secure competitive pricing, ensure consistent quality, and reduce lead times – a major factor when selecting suppliers! These benefits are not benefits alone, as they further bring about risk mitigation, innovation, and contribution to the overall success of the supply chain.
Manufacturing: Another very literally-named step, manufacturing oversees the transformation of raw materials into finished products. This phase encompasses a range of activities such as production planning, scheduling, resource allocation, quality control, and process improvement. The implementation of lean principles and automation throughout the manufacturing process has additionally seen great results such as optimized productivity, minimized waste, and reduced production costs, allowing for a continuous improvement towards streamlined operations and increased competitiveness.
Delivery: Transportation and distribution of products to end customers are the two major facets of the delivery step. It is important to select the appropriate transport modes and logistics providers for the goods or services being provided, all while ensuring that timely and accurate order fulfillment will be achieved in the process. This is most often implemented through the selection of optimized trade routes and efficient warehousing. Moreover, delivery also includes customer service and after-sales support, ensuring that customers receive the necessary assistance and addressing any issues promptly.
Return and reverse logistics: Should there be any returns, repairs, or recycling necessary after delivery has taken place, the return and reverse logistics step comes into play. Efficient reverse logistics processes facilitate the management of returned products, their proper disposition, and the processing of warranty claims. While the aim is to avoid this step, managing customer returns effectively is crucial for enhancing customer satisfaction without running into any unnecessary costs. This can also support sustainability initiatives, such as reducing waste and maximizing the value of the returned products.
How Does Supply Chain Management Work?
Let us further unpack the interconnected processes of supply chain management to help uncover how it works altogether. It is also important to note that when these various processes are interwoven with each other and perform at their optimal levels, grand effects such as cost savings, improved customer service, and a stronger competitive advantage are bound to take shape!
Demand Forecasting: Taking place during the planning phase, demand forecasting involves estimating future customer demand for products or services. Have a read through Intuendi’s article on demand forecasting to learn how it works, its benefits, and more! When demand is accurately forecasted, organizations are able to plan their procurement, production, and inventory levels in accordance, allowing for the avoidance of excess or insufficient stock situations.
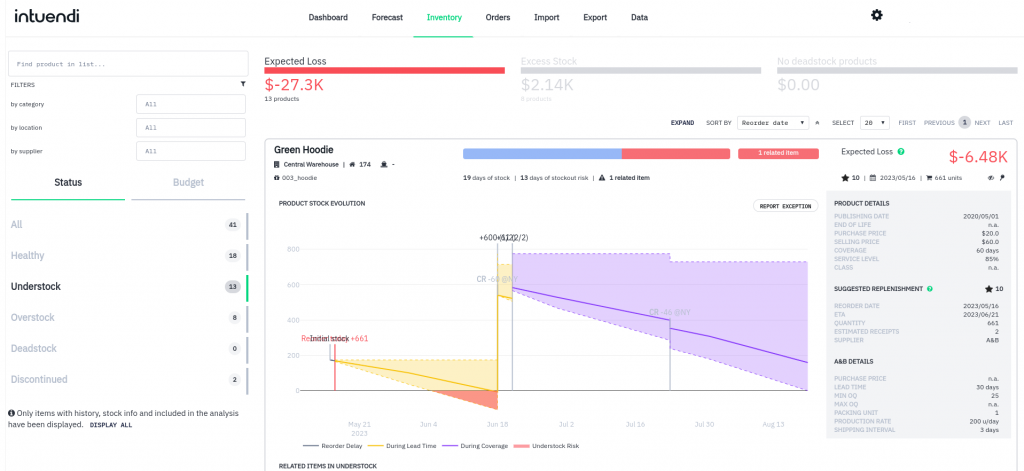
Inventory Management: Focused on optimizing inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing holding costs, inventory management involves determining appropriate stock levels, replenishment strategies, and safety stock requirements. Take a look at our inventory control blog to learn more about the various techniques and features of this important step. Efficient inventory management procedures ensure product availability, reduced stock-outs, and you guessed it -enhanced customer satisfaction!
Production Scheduling: The aim of production scheduling is to optimize the allocation of resources, equipment, and labor to meet customer demand efficiently through creating a timeline for production activities, sequencing tasks, and coordinating workflows. The optimization is achieved by minimizing idle time and optimizing machine utilization by aligning these processes with production capacity and production demand.
Types of Supply Chain Management
Now that we have looked at the various procedures and steps taken during the supply chain, let us focus our attention on the different approaches one can take in managing their supply chain:
Traditional Supply Chain: Characterised by a rigid, sequential, and linear flow of activities, traditional supply chain management focuses on efficiency and cost reduction. These supply chains typically involve long lead times and batch production methods. The emphasis is placed on optimizing individual components within the supply chain rather than the entire supply chain itself. They are most suitable for stable and predictable market conditions, strengthened by their logical flow of procedures.
Lean Supply Chain: As it might be implied by its name, lean supply chain aims on reducing waste, and therefore costs, through the elimination of non-value-adding activities. Lean supply chains may suffer from limited flexibility, however, they perform extremely well in focused optimization of procedures and minimized inventory levels.
Agile Supply Chain: Unlike lean supply chain, agile supply chain prioritizes flexibility, responsiveness, and adaptability to volatile market conditions. Managing agile supply chains is done in a responsive manner, with the ability to adapt to changes in customer demand, market trends, or supply disruptions. These supply chains emphasize real-time visibility, fast decision-making, and rapid reconfiguration of resources. However, this does come with the added cost of higher inventory levels and anything else that may need flexibility.
Hybrid Supply Chain: Combining elements from the 3 approaches above, the goal of the hybrid supply chain is to create a more balanced and adaptable supply chain model, tailoring the strategy used in accordance with product characteristics, demand patterns, and market dynamics.
The 7 R’s of Supply Chain Management
Recapping all that you have read until this point, let us summarise the main features of the supply chain into 7 memorable R’s!
- Right product: The supply chain would not be able to begin without the right product to sell to consumers as the end goal. Ensuring that the correct product is available is essential for meeting customer needs. This calls for a keen understanding of consumer preference and results in customer satisfaction, strong sales, and a competitive edge.
- Right quantity: A crucial element of supply chain management is ensuring that the right amount of stock is available so as to not run into any issues of over or understocking. Balancing supply and demand ensures that customers’ needs are met while carrying costs or lost sales are minimized.
- Right condition: Delivering products in their expected quality and condition! It is important to take proper care, storage, and transportation practices of the products to preserve their integrity throughout the supply chain. Quality products equal quality customer experiences!
- Right place: Taking multiple precautions during the planning phase, it is imperative that the correct product is delivered to the correct place! Optimizing logistics and distribution networks ensure timely deliveries to desired locations.
- Right time: Above and beyond being delivered to the correct location, delivering products at the right time is just as crucial for meeting customer expectations and demand! Timeliness includes both the overall order fulfillment cycle time, as well as adherence to specific delivery schedules or deadlines.
- Right customer: Understanding the specific needs, preferences, and characteristics of the target customers is essential for tailoring the supply chain to their needs. By focusing on the right customer, organizations can provide personalized experiences, develop customer loyalty, and drive repeat business!
- Right cost: Last, but not least, providing the right cost to your customers creates a satisfied, and thus, a repeat customer. However, this should also mean that you are turning a profit! Achieving the right cost involves managing the supply chain’s financial aspects to ensure profitability and cost-effectiveness, which includes optimizing procurement practices, controlling production costs, and managing transportation expenses.
Why is Supply Chain Management Important?
Supply chain management is vital for driving business success, especially when improved operational efficiency and satisfied customers lie at the forefront. Effective supply chain management should minimize costs, optimize resources, and enhance productivity to result in reduced expenses and increased profitability. Moreover, a well-managed supply chain enables organizations to respond swiftly to changing market conditions, mitigate risks, and provide a competitive advantage. Intuendi is a supply chain management solution designed specifically to help decision-makers improve their supply chain efficiency. Contact us to learn more.