SKU codes have transformed the world of inventory management, allowing businesses to easily identify and track any item within their inventory. This article will be exploring all that you need to know about SKUs – their definition, their components and structure, and how their product identification capabilities are used in inventory management.
Intuendi defines an SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) as a code used to uniquely identify the individual items that make up any one company’s inventory. Think of it like an ID number, but instead of being used for people, it is as a machine-readable code used for stock and goods. This code, usually presented in 8-12 characters written in alphanumeric form, contains all necessary information about a single item in your stock, such as pricing, sizing, and product description. The SKU is furthermore used as an inventory tracking mechanism.
SKU Components and Structure
SKUs are usually comprised of indicators pointing toward a product’s physical design and appearance. Let us look at a working example:
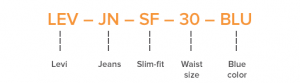
Consider yourself the manager of a retail outlet store, UNIQ, which specializes in the selling of basic clothing items. You offer a range of 3 different types of shirts: T-shirts, Button-ups, and Vests. Use an acronym to provide a description for each shirt type: T-shirt (TS), Button-Ups (BU), and Vests (VE). Each shirt variety is available in 4 colors, which forms the next section of the SKU components: Blue (BLU), Brown (BRO), White (WHI), and Black (BLA). You additionally offer a variety of sizes for shirts from size 4 to size 16.
Combine each factor of the SKU code followed by a sequential number that reveals how many items are available from the shirt section with the same characteristics. Your full SKU for the first product should look something like this:
TSBLU040001
TSBLU040002
TSBLU040003
Another shirt product’s SKU code might look like this:
BUBRO120001
BUBRO120002
BUBRO120003
The same logic should be applied to the remaining shirt products within your inventory. Feel free to adjust your SKU coding method to better suit your company and its customers. Should your customers prefer certain brands over others, this could be factored in as a characteristic of your SKU coding. Take the picture below as an example of a trousers retailer.
While there are important coding techniques to adhere to, there are, however, some to avoid:
- The first two characters should be your top identifiers
- Avoid starting an SKU number with ‘0’
- Avoid using manufacturer numbers in your SKU code
- Do not reuse old SKU product codes from past product lines
- Begin your SKU with letters first
- Avoid using special characters or symbols within your SKU code
- Stick to the most important information and do not overcomplicate it
Product Identification
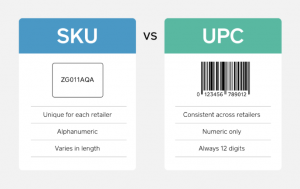
An SKU differs from a UPC (Universal Product Code), as an SKU number is uniquely designed for the use of your store only. It can have varying lengths, and both letters and numbers within the code. A UPC, on the other hand, exists consistently across retailers, is only numeric in form, and always consists of 12 digits. As the above paragraph illustrates, product identification is made simpler and more efficient with the help of SKU product codes, which allows for amplified inventory tracking, both physically and digitally.
Inventory Management
Inventory tracking is the predominant use of SKU codes. Lost sales often occur as a result of poor inventory management, whether it takes shape in the form of stock-outs or even overstocking. With widespread competition and constant changes in the economic and social climate of the world, advanced inventory management technology is becoming crucial for a company’s success. The more insights you have about which products perform the best and when the easier it will be to make informed decisions to help meet customer demand without running into overstocking or understocking situations. Let us identify some of the ways in which SKU codes aid in inventory management:
With the unique identification code that SKUs provide, it becomes much easier to accurately track individual products. Integrated with the use of barcodes, SKUs record product activity, whether they are entering or leaving your stock. This allows for accurate, real-time recording of inventory levels and quantities and provides real-time information to aid in determining when new stock should be reordered and replenished.
Not only are you able to track inventory whereabouts with the help of the number of SKUs, but the product details as well. This, in turn, with the help of an efficient categorization and sorting mechanism, makes tracking their whereabouts a much simpler task!
Application in Retail
As we have already elaborated on the benefits of SKUs in product identification and inventory management, let us delve into the additional uses of SKUs in retail and SKU marketing:
Organization: Maintaining an easy-to-navigate system can form much of the attraction, not only to the retailer and staff members but to the customers! After a long day of shopping, with tantrum-throwing toddlers, the tired parents do not want to exert more energy and effort on finding the product they are looking for. With the help of SKU codes, retailers are able to better organize stock according to their similar features and characteristics, simplifying the searching process for clients, and driving their customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Order Fulfillment: Whether customers place orders for products physically, in-store, or online, SKUs ensure that the customer receives the correct product through location and selection features associated with the unique product code.
Marketing: SKU marketing involves tracking how well certain products have sold following a directed marketing effort. This, therefore, allows retailers to assess how effective and successful their marketing strategies have been.
Losses and Theft: Losing products to theft and poor inventory management can form part of a retailer’s largest frustrations. However, the SKU in retail can be utilized within loss prevention strategies. Through the inventory tracking benefits provided by SKUs, retailers are able to closely monitor inventory movements, which makes detecting discrepancies a much easier task.
The Value of SKU Codes
If your company finds itself in hot water, drowning in inventory management issues and a lack of tracking mechanisms, perhaps your first step to recovery should involve implementing an SKU strategy. These unique identifiers strengthen categorizing, and therefore, tracking efforts, inventory controlling and ultimately amplifying the consumer experience when a customer walks into your store. SKUs can be used across various industries, such as clothing retail, electronics, and groceries, with an easy-to-follow, standardized product identification format. Ensuring accurate stock levels, optimized order fulfillment, and insightful sales analysis are some of the top benefits enjoyed by the users of SKU codes.