Stock-outs, or situations where products are unavailable when customers seek to purchase them, pose significant challenges across industries. Beyond being a logistical inconvenience, they can harm a business’s profitability, erode customer loyalty, and disrupt overall supply chain efficiency. Effectively managing and preventing stock-outs requires a deep understanding of their causes, types, and the implementation of strategic management practices to transform this common challenge into an opportunity for operational excellence.
What are Stock-outs?
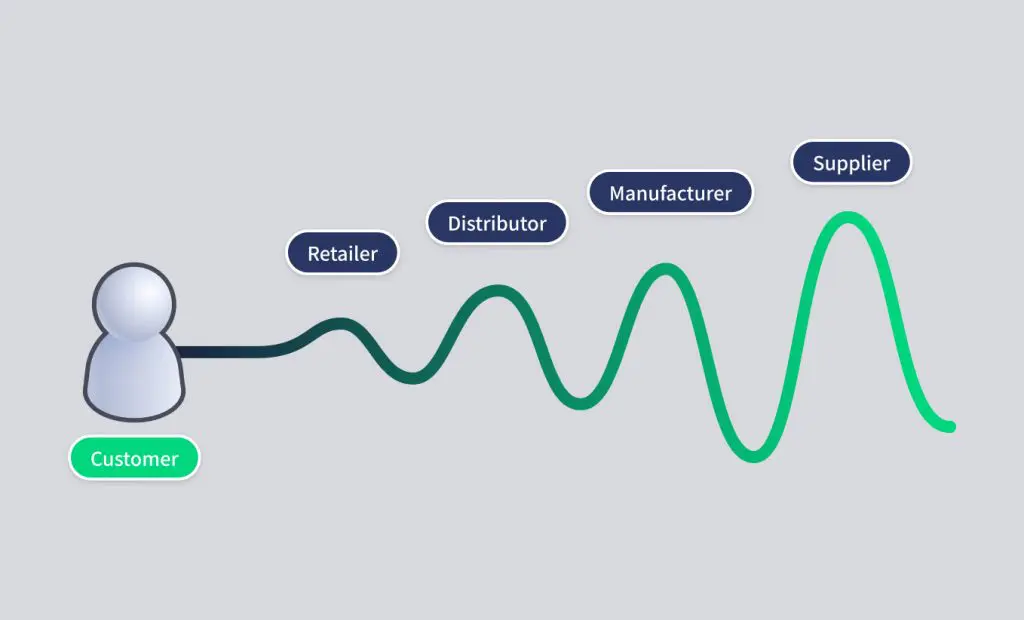
A “stock-out” situation occurs when the demand for a product exceeds its available supply, rendering it unavailable for sale or use. This imbalance between supply and demand often reflects deeper issues within the supply chain, such as forecasting inaccuracies, delays, or mismanagement of inventory. Beyond empty shelves, inventory shortage highlight operational vulnerabilities that can impact customer satisfaction and long-term business performance. By recognising and addressing these imbalances, businesses can optimise their inventory strategies, maintain customer trust, and ensure smooth operational continuity.
Types of Stock-Outs
Lack of stock occur in various forms, each with unique implications. Temporary stock-outs are short-lived disruptions often triggered by sudden spikes in demand or minor supply chain delays. While they may be resolved quickly, they can still lead to lost sales and customer frustration if not managed promptly. In contrast, seasonal stock-outs are predictable and tied to specific times of the year, such as holiday shopping periods or seasonal product launches. These situations require meticulous planning and robust inventory management to meet demand without excess stock accumulation. Finally, prolonged stock-outs represent more serious, long-term shortages caused by significant supply chain disruptions, poor forecasting, or systemic inventory failures. These can have lasting negative effects on customer trust, competitive positioning, and market share. Understanding these distinct types allows businesses to adopt tailored strategies for managing and mitigating each scenario effectively.
Main Causes of Stock-out Issues
Stock depletion are often the result of interconnected internal and external factors, requiring a strategic approach to address them. One of the most common causes is demand forecasting errors, where inaccurate predictions lead to understocking or overstocking. Underestimating demand results in product shortages, while overestimating ties up capital and risks obsolescence. Inventory allocation problems also contribute to stock-outs, as uneven distribution across warehouses or retail locations can cause shortages in one area while others remain overstocked. Supplier-related issues, such as delays, inconsistent deliveries, or poor communication, further exacerbate the problem by disrupting the flow of goods. Finally, safety stock mismanagement plays a critical role; while buffer inventory can cushion against unexpected demand or delays, insufficient safety stock increases the risk of stock-outs, whereas excessive stock leads to unnecessary costs. To effectively address these causes, businesses must improve their demand forecasting techniques, optimise inventory allocation, foster stronger supplier relationships, and strategically manage safety stock levels.
By understanding these causes and adopting a proactive approach, businesses can not only reduce the frequency of stock-outs but also improve operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall supply chain resilience.
Demand Forecasting Errors
Accurate demand forecasting is essential but inherently complex, influenced by seasonal trends, economic changes, marketing efforts, and sudden demand spikes. Errors arise from relying solely on historical data, using inadequate methodologies, or failing to integrate real-time market and sales data. For example, businesses may overlook the impact of new marketing campaigns or competitor actions, causing discrepancies between forecasts and actual demand. Compounding these issues are a lack of advanced analytics tools and skilled personnel. Improving forecasting accuracy requires leveraging real-time data, advanced analytics, and fostering collaboration across departments to better anticipate and respond to fluctuating demand.
Inventory Allocation Problems
Inventory allocation ensures products are distributed across locations to meet demand, but poor allocation can cause overstocking in some areas and stock-outs in others. This often results from inaccurate demand assessment, transportation delays, or warehousing inefficiencies. For instance, sending excess stock to flagship stores while neglecting emerging demand in smaller locations can lead to missed sales opportunities. Poor inventory visibility further complicates timely decision-making. Addressing these issues involves using data analytics for location-specific demand forecasting, improving inventory tracking systems, and streamlining distribution networks to ensure products reach the right locations efficiently.
Supplier Relationship Management
Strong supplier relationships are vital for inventory stability, as issues like delivery delays, miscommunication, or production problems can disrupt supply chains and cause stock-outs. A lack of transparency regarding lead times or order details can exacerbate shortages. For example, unclear shipment schedules can leave businesses without stock before replenishment arrives. Building trust-based supplier partnerships improves communication, enhances flexibility, and ensures quicker resolution of disruptions. Businesses that prioritise supplier collaboration are better equipped to maintain consistent inventory levels and reduce supply chain risks.
Over- or Under-Stocked Safety Stock
Safety stock acts as a buffer against demand fluctuations and supply delays but requires careful management. Overstocking ties up capital, raises storage costs, and increases the risk of obsolescence, while understocking leaves businesses vulnerable to stock-outs. The challenge lies in determining optimal safety stock levels based on factors like lead time variability, forecast accuracy, and desired service levels. Companies can strike this balance using advanced inventory management tools to calculate precise safety stock levels, reducing stock-out risks while avoiding excess inventory costs.
The Impact of Stockouts on Business Performance
Stock-outs affect more than immediate sales loss; they impact financial performance, customer experience, and operational efficiency. Customers often turn to alternatives, leading to both short-term revenue loss and long-term consequences, such as damaged brand perception and reduced customer loyalty. Effective stock management is essential to mitigate these risks and ensure business sustainability.
Effect on Sales and Revenue
Stock-outs lead to immediate sales and revenue losses, particularly in competitive sectors where customers can easily switch to alternatives. Beyond missed sales opportunities, frequent stock-outs erode customer trust, reducing repeat purchases and lifetime value. For impulse-driven or seasonal purchases, such as retail or e-commerce during peak periods, stock-outs result in significant income loss. In e-commerce, unavailable products cause abandoned carts, lower conversion rates, and reduced profitability, cumulatively impacting overall revenue and market share.
Customer Experience and Loyalty
Stock-outs damage customer experience and brand loyalty, creating frustration and disappointment when desired products are unavailable. Repeated stock-outs can make businesses appear unreliable, prompting customers to seek alternatives. Negative experiences are quickly amplified through online reviews, harming brand reputation. Conversely, consistent product availability fosters trust, enhances customer satisfaction, and encourages repeat purchases and word-of-mouth referrals, strengthening long-term loyalty and brand image.
Specific Impact on E-commerce
E-commerce businesses face heightened risks from stock-outs due to customer expectations for real-time inventory updates and immediate availability. Online shoppers, with instant alternatives at their fingertips, are less forgiving and often switch to competitors. Frequent stock-outs can lower search engine rankings, as platforms prioritise available products, reducing visibility and sales opportunities. To address this, e-commerce businesses must adopt robust inventory management systems, real-time stock updates, and efficient supply chain logistics to meet customer expectations and maintain competitiveness.
Strategies to Prevent Stockouts Situations
Preventing stock-outs involves a proactive approach to inventory management through data-driven insights, technology, and streamlined operations. By anticipating demand fluctuations, optimising stock levels, and improving supply chain processes, businesses can ensure consistent product availability. These strategies reduce stock-out risks, enhance operational efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction.
Accurate Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting is essential for preventing stock-outs by predicting customer needs with precision. Businesses can leverage historical sales data, real-time market insights, and factors like seasonality or promotions to improve forecasts. Advanced techniques, including statistical modelling and machine learning algorithms, offer deeper insights and adaptability to changing conditions. Collaborative forecasting, integrating inputs from sales, marketing, and operations, further enhances accuracy. This comprehensive approach ensures inventory levels align closely with anticipated demand.
Optimising Inventory Allocation
Effective inventory allocation ensures products are positioned where demand is highest. By segmenting inventory based on product velocity, demand variability, and geography, businesses can distribute stock strategically. High-demand items are placed closer to customers to minimise lead times, while slower-moving items can be centrally managed to optimise costs. Real-time inventory systems provide visibility, enabling dynamic reallocation to address shifting demand and prevent localised stock-outs or overstocking.
Automating Replenishment with AI
AI-driven replenishment systems enhance stock management by analysing large datasets, predicting future stock needs, and automating reordering processes. Machine learning algorithms refine these predictions over time, improving accuracy and adapting to demand shifts. AI can proactively identify rising demand and trigger purchase orders before shortages occur, reducing manual errors and streamlining operations. This automation cuts lead times, ensures optimised stock levels, and enhances supply chain efficiency.
Managing and Optimising Safety Stock
Safety stock serves as a critical buffer against demand and supply uncertainties. Optimising safety stock levels involves balancing inventory to meet unexpected spikes while avoiding overstocking costs. Statistical models consider factors like demand variability, lead time, and desired service levels to calculate ideal safety stock. Advanced systems automate these calculations, dynamically adjusting buffer levels based on real-time conditions. Regularly reviewing and refining safety stock strategies ensures businesses can mitigate stock-outs without excessive holding costs.
Stock-Out Management Techniques
When stock-outs occur despite preventive measures, businesses must employ strategies to minimise customer impact and maintain flexibility. Key techniques include proactive communication, offering alternative fulfilment options, and efficiently leveraging existing resources to meet customer needs.
Proactive Customer Communication
Transparency amidst product unavailability builds trust and mitigates frustration. Businesses can provide real-time stock updates on websites, send product availability notifications, and offer alternatives like similar products or pre-orders. For instance, displaying restock dates and allowing email sign-ups for updates retains customer interest and secures future sales. Effective communication channels include email, social media, and website alerts to ensure timely and preferred customer outreach.
Flexible Fulfilment Options
Flexible fulfilment helps meet demand when products are unavailable in specific locations. Methods such as drop-shipping allow products to be sent directly from suppliers, bypassing in-house inventory. Similarly, inter-store transfers move surplus inventory from one location to another experiencing shortages. Leveraging robust inventory management systems enables businesses to quickly implement these solutions, ensuring customer satisfaction and minimising delays.
Inter-Store Transfer Strategies
Inter-store transfers address localised item absence by redistributing inventory within a company’s network. Real-time inventory visibility and efficient logistics systems enable swift movement of stock between locations. Clear protocols for initiating, managing, and tracking transfers ensure operational efficiency. By optimising inter-store transfers, businesses can maintain product availability and meet customer demand across their network.
Using Pricing as a Demand Lever
Strategic pricing adjustments help control demand and manage stock levels. Raising prices on high-demand items moderates sales, preventing rapid inventory depletion. Meanwhile, discounts or promotions on substitute products encourage customers to choose alternatives, easing pressure on limited inventory. Dynamic pricing systems, which adjust prices in real time based on demand and stock levels, allow businesses to balance inventory management, revenue optimisation, and customer satisfaction.
Key Technologies for Stock-Out Management
Technology is critical for managing stock-outs, offering tools to predict demand, track inventory, and automate replenishment. Solutions like inventory management software, advanced analytics, and automation systems help businesses minimise stock-outs and improve supply chain efficiency.
Inventory Management Software
Robust inventory management software provides real-time visibility into stock levels, automates reorder points, and enables demand forecasting. Integration with platforms like e-commerce and POS systems ensures data accuracy and seamless communication across channels. With features like stock alerts and analytics, businesses can track KPIs, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to reduce errors and prevent stock-outs.
AI and Machine Learning for Stock Prediction
AI and machine learning enhance stock management by analysing historical data, market trends, and seasonal patterns to predict demand with precision. These systems adapt to changing conditions, using real-time insights to anticipate surges and automate replenishment before stock-outs occur. Predictive analytics supports proactive decision-making, improving supply chain efficiency and ensuring product availability.
Logistics Automation Solutions
Logistics automation streamlines warehouse operations and reduces lead times through technologies like automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), robotic picking, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). These systems enhance accuracy, reduce errors, and accelerate order fulfilment. By automating processes like sorting and packaging, businesses improve operational efficiency, lower costs, and reduce the risk of stock-outs caused by logistical delays.
Essential KPIs to Monitor to Prevent Stock-Outs
Preventing stock-outs relies on tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) that provide critical insights into inventory health and operational efficiency. Monitoring the inventory turnover rate helps businesses understand how quickly stock is sold and replenished, where a high rate indicates strong sales and efficient management, while a low rate may point to overstocking or slow-moving products. Equally important is supplier lead time, which measures the time it takes for suppliers to deliver goods after an order is placed; managing lead time variations is essential to ensure timely replenishment and avoid disruptions. The order fulfilment rate reflects operational efficiency by measuring the percentage of customer orders delivered on time and without errors, indicating the reliability of inventory and logistics processes.
Additionally, tracking the backorder rate helps identify the frequency and severity of stock-outs, signalling the need for improved forecasting and replenishment strategies. Finally, the lost sales rate quantifies the percentage of potential sales missed due to stock-outs, providing a clear measure of their financial impact. Through efforts to consistently monitor these KPIs, businesses can identify weaknesses, optimise stock levels, and implement targeted improvements. Leveraging these insights, alongside accurate demand forecasting, strong supplier relationships, and advanced technologies, ensures operational efficiency, enhances customer satisfaction, and maintains a competitive edge in the market.